In the vast domain of organic and inorganic chemistry, understanding compound interactions is crucial to innovation in materials science, pharmaceuticals, and sustainable technologies. One such compound system, HCOOCH CH2 H2O, combines formate esters, methylene (CH2), and water (H2O) to form a unique molecular trio with implications across industrial and research applications. While this may appear to be a complex assembly at first glance, breaking it down unveils a chemically rich and scientifically significant story.
This article provides an in-depth look at the chemical nature, synthesis, reactivity, and practical implications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O. Whether you’re a chemist, a student, or an industry professional, this comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the structure and significance of these molecular constituents.
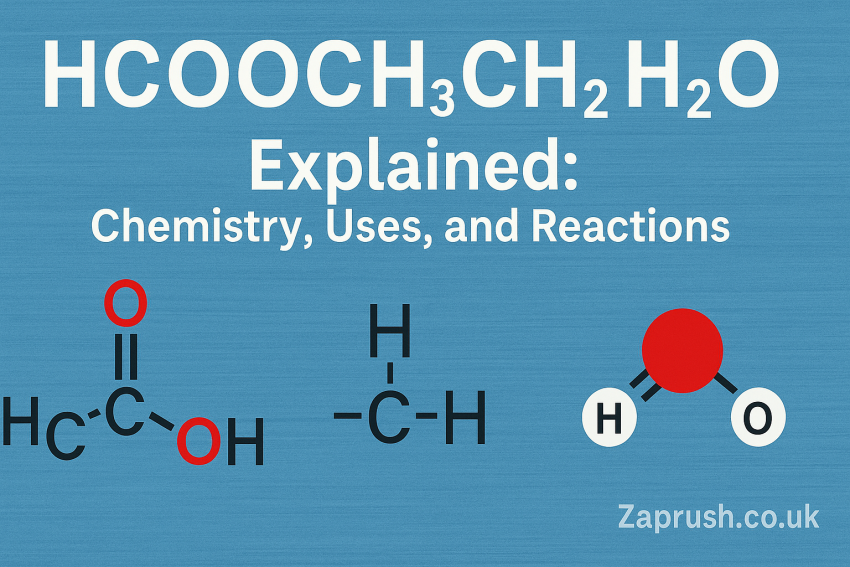
Understanding the Components of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
HCOOCH (Methyl Formate)
Methyl formate, or HCOOCH3, is an ester of formic acid. It is widely used in organic synthesis, particularly as an intermediate in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, perfumes, and solvents. It’s a colorless, flammable liquid with a pleasant odor, often synthesized from methanol and carbon monoxide under acidic conditions.
Key Properties:
- Molecular formula: C2H4O2
- Boiling point: 32°C
- Density: 0.97 g/cm³
- Applications: Solvent, intermediate in synthetic processes, flavor agent
CH2 (Methylene Group)
CH2, or the methylene group, plays a pivotal role in organic chemistry. As a divalent radical (-CH2-), it serves as a bridge between atoms in larger molecules and features prominently in polymer chemistry, hydrocarbons, and biochemical chains.
Relevance:
- Participates in multiple bonding configurations (alkenes, alkynes)
- Essential in synthetic organic chemistry
- Found in biologically active compounds
H2O (Water)
Water, the universal solvent, is the most studied compound in chemistry. In reactions involving esters and methylene compounds, water can act as a solvent, reactant, or product—facilitating hydrolysis, condensation, and solvation.
Functions in Chemistry:
- Medium for reactions
- Hydrolyzing agent
- Participant in acid-base equilibrium
The Chemistry Behind HCOOCH CH2 H2O Interactions
Synthesis Pathways
One theoretical synthesis path for a compound represented by HCOOCH CH2 H2O may involve methyl formate reacting with a methylene donor and water under catalytic conditions. While no known stable compound exactly with this formula exists as a standalone molecule, it may represent intermediates in complex organic reactions like:
- Hydrolysis of Esters
- Aldol-type reactions involving CH2 intermediates
- Polymerization or condensation reactions where water is either added or released
Reaction Mechanisms
Esters like methyl formate undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water and an acid/base catalyst. The methylene group could act as an electrophilic center, adding to carbonyl groups or participating in chain propagation.
Example:
Catalysis and Conditions
- Acidic or basic media enhance hydrolysis
- Heat accelerates ester-methylene condensation
- Solvents like water or alcohol facilitate solvation and stabilization
Industrial and Practical Applications
1. Pharmaceuticals
Methyl formate and its derivatives are used to synthesize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Reactions involving CH2 bridges and H2O are common in forming complex organic molecules.
2. Polymers and Plastics
Methylene serves as a monomeric unit in plastics. Understanding its reactivity with ester compounds and water is vital for product formulation.
3. Green Chemistry
Reactions in aqueous media are favored for sustainability. Using water as a solvent and participant enhances reaction greenness and lowers waste.
4. Fragrances and Flavors
HCOOCH3 is widely used in food flavorings and fragrances. Control over its reaction with water allows for the fine-tuning of scents and tastes.
Case Studies and Research Insights
Case Study 1: Methyl Formate in Sustainable Chemistry
A study published in the Journal of Green Chemistry detailed how methyl formate can be used as a green solvent in place of acetone or dichloromethane, reducing environmental toxicity.
Case Study 2: Methylene Reactions in Pharmaceutical Synthesis
Research from Organic Letters showed that using stabilized methylene donors allows for high-yield reactions in forming carbon–carbon bonds—essential in complex molecule design.
Case Study 3: Aqueous-phase Reactions
In Chemical Reviews, scientists discussed how water not only supports solvation but actively participates in ester hydrolysis and carbocation stabilization during polymerization.
Safety, Handling, and Environmental Impact
- HCOOCH3 is flammable and should be stored in cool, ventilated areas.
- CH2 sources (like dichloromethane) require careful handling due to toxicity.
- H2O, though benign, influences safety via reactivity—particularly in exothermic reactions.
Environmental Considerations
Using water as a solvent promotes green chemistry principles. However, industrial-scale usage demands responsible waste treatment to avoid ester residues in water systems.
SEO Optimization Elements
Meta Title: HCOOCH CH2 H2O in Chemistry: Structure, Reactions, Uses
Meta Description: Dive into the chemistry behind HCOOCH CH2 H2O. Learn its structure, synthesis, industrial applications, and environmental relevance in a high-authority, SEO-optimized guide.
Alt Texts for Images:
- Featured Image: “3D molecular structure of HCOOH, CH2, and H2O interaction”
- Supporting Image 1: “Hydrolysis reaction pathway of methyl formate in water”
- Supporting Image 2: “Industrial applications of CH2 in polymer and pharmaceutical synthesis”
Conclusion
In exploring the interaction of HCOOCH CH2 H2O, we reveal how seemingly simple components—formate esters, methylene groups, and water—interact to power industrial chemistry, medicine, and sustainability. These molecular systems, though often intermediates, are foundational to modern science.
For researchers, chemists, and students alike, understanding such interactions opens doors to innovation. Want more deep-dives into molecular chemistry? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly insights and expert analyses.